A flat bed CNC machine refers to a type of computer numerical control (CNC) machine tool that features a horizontal bed design. In this design, the workpiece is placed horizontally on a flat bed for machining operations. Here are some key points about flat bed CNC machines:
Versatility: Flat bed CNC machines are versatile and can handle a wide range of machining operations, such as turning, milling, drilling, tapping, and more. They can be customized with various tooling options to accommodate different machining requirements.
Stability and Rigidity: Flat bed machines provide a stable and rigid platform for machining operations. The horizontal bed design offers good support to the workpiece and reduces vibrations, leading to improved machining accuracy and surface finish.
Accessibility: The horizontal bed design of a flat bed CNC machine allows for easy access to the workpiece. Operators can efficiently load and unload workpieces, set up tools, and monitor the machining process.
Chip Evacuation: While chip evacuation can be a consideration on flat bed machines, they typically utilize chip conveyors, coolant systems, and other mechanisms to remove chips from the machining area. Proper chip evacuation helps maintain machining efficiency and prolong tool life.
Floor Space Requirement: Flat bed CNC machines generally require a larger floor space compared to inclined bed machines. The footprint of a flat bed machine can vary depending on the size and configuration of the machine, and it's essential to consider the available space in the workshop when selecting a machine.
Applicability: Flat bed CNC machines are widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, general engineering, and more. They can handle both small and large workpieces, making them suitable for a range of production requirements.
Cost: Flat bed machines can vary in terms of cost depending on factors such as size, configuration, and additional features. It's important to consider the specific machining needs and budget constraints when selecting a flat bed CNC machine.
Flat bed CNC machines are a common choice in many manufacturing facilities for their versatility, stability, and accessibility. They offer the capability to perform a wide range of machining operations and can be tailored to meet specific production requirements. However, it's important to evaluate the specific needs of your application and consider factors such as space availability and cost before investing in a flat bed CNC machine.
Flat Bed CNC Machine, Flat Bed Lathe Ningbo Leyan Machinery Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.cncleyan.com
The SIS system is a real-time management and monitoring system that implements a comprehensive optimization service for the production process. It integrates all DCS systems, Programmable Logic Control (PLC) systems and other computer process control systems (PCS) down to the entire plant. , Upward and MIS system organic combination to form a complete plant-wide information system. It can be said that the SIS system is a bridge connecting the whole plant process control system and management system. The real-time database is the basis of the power plant SIS architecture. At present, the power plant information (PI) real-time database system developed by the US OSI soft software company is more commonly used in power plants. Pl is used for automatic collection, storage and monitoring of power plant data. As a large real-time database and historical database, PI can store years of multi-year data at each process point. It provides a clear and accurate picture of operating conditions. The user can not only view the current production status of the power plant, but also review the past production conditions. It can be said that PI fully meets the requirements of the SIS system database with large capacity, high reliability, and fast response speed. Claim. This article elaborated the function of each module of PI system, and discussed the application of Pl database in power plant SIS system.
Second, PI system structure
PI system can realize the structure configuration of C/S and B/S, and the intelligent structure it uses can run under a variety of system configurations. The PI server software provides real-time data collection and storage, and the PI client software allows users to maximize the processing of production information.
Multiple PI servers can be installed and operated in power plants and group companies, with flexible capacity configurations ranging from thousands of small systems to hundreds of thousands of large systems. Each PI server can be connected to one or more field control systems at the same time and can be written to describe any real-time device or database. PI can be used to transfer data information between multiple different vendors' products. This flexible and powerful structure provides a great degree of freedom for optimizing the structural design of real-time information systems.
As long as the machine performance and network performance of the PT server software are installed, the number of users supported by the PT is unlimited. Most of the applications used on the PI are software products for PT system clients. These applications require less system resources than the terminal dialog or X-Windows requires to log on to the central host. The PT client uses less network bandwidth than the terminal or X-Windows.
Third, the main function module of PI system
The PI system consists of a series of plant-level monitoring and analysis software modules, which mainly include three types of software: server, client, and interface. The server software is used to collect and store on-site production data. The client software provides secondary application of real-time/historical data. The interface software implements the connection of different control systems and PI systems on site.
3.l PI Server Software Module
PI-UDS is the basic kernel of PI system. As a data server based on Win-dows client application, factory users can use various client application software to connect to PI-UDS to observe those stored in PI archive database or external storage. Data in the system [5]. PI-UDS consists of the following components.
3.1.1 Core Subsystem
The core subsystem mainly includes six parts.
a. The basic library subsystem. In the PI system, points are defined for each process value to be collected. Each point has about 50 attributes. These attributes define how the point data is collected and stored. The basic library subsystem is responsible for maintaining these attributes stored in the point database.
b. Snapshot subsystem. In the PI system, the current value of each point is called a snapshot. The snapshot subsystem is responsible for determining whether the snapshot should be sent to the archive subsystem or replaced by a new snapshot.
c. Archive subsystem. Stores multiple time stamped measurements at each point, such as switching, pressure, flow, temperature, setpoints, and more.
d. Message subsystem. Record the PI-UDS status and error messages in the log file.
e.SQL subsystem. Responsible for processing SQL statement, if you install the COM connector, SQL subsystem can also obtain data from external data sources.
f.COM connects steering gear. When the PI database interacts with external data sources, it acts as an intermediary.
3.1.2 PI Network Manager
The PI Network Manager provides connections between various PI-TinS subsystems residing on the PI Primary Node and also manages the connection between the PI System and client applications.
3.1.3 PI Server Application Module
The PI server includes 3 application modules.
a. Execute the calculation module. Allows users to avoid having to implement complex computing functions in high-level languages. This module allows the user to generate a calculation formula, use a simple algebraic formula, and store it in the library multiple times. The calculation result of the equation equation package can be stored in the same data file as any station number in the PI system. The equation equation package can be directly connected to external functions written in C or Fortran. Most PI systems have a state equation package.
b. Batch processing module. Storing and reading PI system data in a batch context does not rely solely on the time axis. When a batch record is created, it includes some batch information, such as the batch record number, batch ID, product ID, and unit name. The query function will allow the user to query the batch of interest.
c. Alarm service module. Alarm conditions can be set for any station number in the PI system, such as high limit alarms, low limit alarms, deviation alarms, or ROC alarms. These alarms can be sent to the event file in the PI system. Users can filter and view alarm conditions.
3.1.4 Configuration and Management Module
The configuration and management module is used to configure points in the database, monitor data traffic, manage data archiving, set security attributes, and more.
3.2 PI Client Software Module
The client software module is based on a series of customer tool software developed under the Windows operating system. Users can easily read data from the PT database in different formats. These tools enable different users to see the information they care about in the same database. Everyone has their own screens, reports, and analysis capabilities to meet different needs. The following describes some of the major client software.
a. PI-PB software. PR is one of the two major user interface softwares in the PI system. It is a graphical user interface. Users can create various types of screens, including trend graphs, pixels, values, bar graphs, and other dynamic graphs. It supports ODBC. , ActiveX, VBA and other technologies. The purpose of the PR is to allow each person in the power plant to establish his own production operation and management picture in the form of a book on his desktop.
b. PI-DataLink software. It is the second major user interface software in the PI system and implements data exchange between the PI system through embedding menus in Excel or Lotus l-2-3. The user can easily and quickly populate the spreadsheet with real-time and historical data from the PI system without the need for complex "guides". PI-Datalink is widely used, users can use it with Excel to do data analysis and generate reports.
C. PI-API application program interface. API is a set of library functions that can be called by C, Visual Basic and other languages, and can read and write PI-UDS data. The API provides a way for users to programmatically access PT system information. Both PR and Datalink can be used to access the PT database.
d.PT-ActiVe View is a Web client application that allows users to publish pictures generated in PB in a universal browser.
e.PI-ODBC client. Through it, the PI database can communicate with other ODBC-enabled databases, and users can easily access external databases.
f.PI batch client. Allows you to view the data in the PI based on the corresponding relationship in bulk.
g. PI-SQC software is an application in PB that takes data from a PI database or other ODBC database and performs statistical calculations, and then displays the results in a PI-SQC chart.
3.3 PI Interface Software
OSIsoft Software Corporation, as an independent third-party software vendor, can now provide standard interfaces for up to 300 types of products from different manufacturers with different control systems. In addition, the PI system also provides data communication interfaces that support industry standards such as OPC, Modbus, etc.
The interface of PI system is generally realized through the PI-API node machine. The main work of the node machine is that when the scanning section and the node machine as a data source are disconnected due to hardware/software upgrade and other reasons, the PI server resumes normal operation. Then the data transfer node in the buffer queue can configure itself by starting the communication of the PI server, thereby saving a lot of work on the PI server.
Fourth, PI system design principles and data flow
4.1 Design Principles
a. Obtain all relevant data for operations or production.
b. Long-term online data storage.
c. Store data prototypes.
d. The data source is unique.
4.2 Data flow
PI system data flow shown in Figure 1 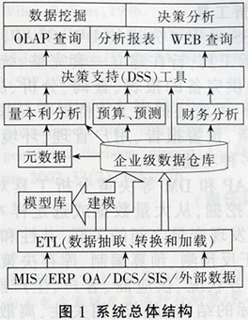
a. Data from the on-site DCS and other data sources are first sent to the PI node's interface program for exception testing. When the data changes beyond the pre-temple of the temples, the data is further transferred, otherwise the data is discarded.
b. The data passed through the exception test is sent to the snapshot subsystem and becomes the new snapshot value. The previous snapshot value is determined by the “Spiral Gate†compression specification to be further transmitted or discarded.
c. Data comes out of the snapshot subsystem and enters the event queue. The data in the event queue is sent to the archive buffer. When the archive is not available, the data can be transferred to a disk file after the queue is full, and then transferred to the archive database after the archive is available.
d. After the data enters the archive buffer, the system stores the data in the buffer in the archive database at regular intervals. This completes the data flow.
V. Application of PI Database in SIS System
The SIS system is based on a decentralized control system and is built on an open database. It aims at safe and economical operation and improves the overall efficiency of the power generation enterprise. It adopts an advanced, applicable, and effective mathematical model to achieve information sharing within the entire power plant and plant-level production. Process information monitoring and scheduling provide real-time and reliable real-time operational data for decision-making of power plant management. At the same time, through comparison and analysis, scientific and rational decision-making schemes can be proposed to make the management decisions of enterprise management more scientific.
The power plant SIS system includes modules for real-time monitoring, plant-level load distribution, real-time performance calculation, operation analysis optimization guidance, main and auxiliary machine state detection, equipment life calculation and status analysis, system fault diagnosis, and other optimization software. Their applications are based on Above the distributed real-time database PI platform, the application data comes from the production site DCS, PLC and other engineering control system PCS. The PI real-time database collects a large amount of real-time production data from the site through various data collection interfaces in an efficient and reliable manner, and at the same time, it can also obtain management data from the management system through a common interface to guide production management. On the other hand, the SIS system provides an open interface to provide real-time/historical data for the MIS system and data calculated/analyzed by the SIS system to support management decision-making. The system is shown in Figure 2. As can be seen from Figure 2, PI real-time database is the core of the entire SIS system, responsible for providing data support for each module, and connecting other control systems [6]. 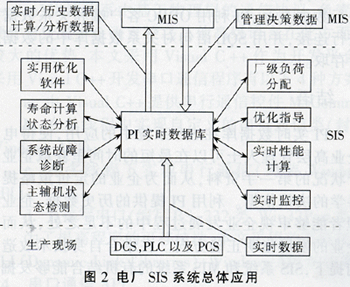
The following describes the specific application of PI in the SIS system.
a. PI removes data from DCS and other data sources in the field and stores it in the snapshot subsystem and archive subsystem. PI provides three ways to take data: connect the DCS system through a standard custom interface provided by PI; connect a PLC system through a unified open interface provided by PI such as OPC, MODBUS/+; and a system that does not provide a standard open interface (non-standard interface ), you can use the application development programming tool API provided by the PI database or SDK programming, and then transfer the connection by the interface computer.
b. Provide data for each software module in the SIS system. Each module uses the PI-API interface to retrieve data from the PI database for various performance calculations and analysis, and saves the calculated data back to the PI database for later invocation.
c. Through the Process Book to configure the way for the whole plant staff to provide a variety of graphical interfaces such as simulation charts, curve trends, parameter maps, and refresh data in real time, to facilitate the staff to query and analyze the data they need.
d. Generate data reports for each major data parameter in the production process through ExCel and Datalink, provide each functional department with various required information, and provide query and print functions. Data reporting using Excel and Datalink can be done in two ways. For a simple report with a fixed format, you can set the report directly in Excel, and then access the data through the PI menu embedded in Excel in Datalink. This method is relatively simple, you can achieve the production of reports without programming, but require customers to understand Datalink. For flexible report formats, because the report format is not fixed, it cannot be directly set in Excel. This requires VBA programming in Excel. Through VBA programming, you can fill in the required data in the specified form in Excel. , and flexibly change the settings of the ranks. In order to obtain the data in the PI database in VBA, you need to use the PI-API interface function, and use the functions that Datalink brings (these functions are in one-to-one correspondence with the menu items in the PI menu that Datalink embeds in Excel. Use these functions to implement all the functions of Datalink.) This method of producing reports is quite demanding for developers, but it relieves the pressure on customers. Customers can do report operations without having to understand Datalink.
e. The various interfaces generated by PB are published through Web pages through ActiveView for easy query.
In order to interact with the relational database in the MIS system and other systems, PI uses an ODBC client and a relational database to connect and use SOL statements to access data in a relational database.
6. Conclusion
The application of the PI real-time database in the SlS system enables the top management personnel of the power company to obtain first-hand information on the production status of the enterprise in the shortest time, thus providing a scientific decision-making basis for the pricing strategy of the enterprise. Using the historical data provided by PI, business managers can examine the deficiencies in the development process of the company, thus indicating the right direction for the development of the company. Under the premise of combining its own technological transformation, the organic combination of the SIS system and the MIS system can uncover the production potential of enterprises, reduce production costs, and increase economic efficiency, making enterprises stand invincible in the fierce market competition and continue to grow and develop. .
PI Database and Its Application in Power Plant SIS
With the deepening of the reform of the power system, separation of plants and networks and competitive bidding for the Internet have become an inevitable trend. This requires that each power plant must pay attention to integrating the company's existing software and hardware resources, achieve information sharing within the entire power plant, and achieve control and control integration. However, DCS (Distributed Control System) and other distributed control systems in power plants are often distributed on different computers or control systems, and they are not only uniformly stored and used. This makes each control system an isolated island of information, making it difficult to analyze the data comprehensively, or even causing simple problems because it is impossible to concentrate on sufficient data and cannot solve the problem. There has been much research on information systems. At present, many domestic power plants have established a Management Information System (MIS) for management information systems. However, because the integration of control information and management information is not well resolved, the management and control of milking make it difficult to raise the management level to a higher level, and the management efficiency is hard to achieve. Therefore, the Supewisory System (SIS) of the plant's plant level monitoring system has been rapidly developed.